


 , Silap Bopha2, Stefano Nativi4, Joost van Bemmelen5, Mattia Santoro4, Guido Colangeli5, Xu Zhe3, Guo Zhifeng6, Laia Romero7, Bernat Martinez7, Zhao Jing1, Tian Chuanzhao1
, Silap Bopha2, Stefano Nativi4, Joost van Bemmelen5, Mattia Santoro4, Guido Colangeli5, Xu Zhe3, Guo Zhifeng6, Laia Romero7, Bernat Martinez7, Zhao Jing1, Tian Chuanzhao1
2. Ministry of Science and Technology of Lao P. D. R., Vientiane 2786;
3. National Satellite Meteorological Centre of China, Beijing 100081;
4. CNR-IIA, Sesto Fiorentino 50019;
5. European Space Agency, Frascati 00044;
6. ChinaRS Co. Ltd, Beijing 100101;
7. isardSAT S. L., Barcelona 08042

There are more than 60 countries and regions along the Belt and Road (BAR) area which connecting the three continents of Europe, Asia, and Africa. As the sign of national comprehensive in this area, space technology also show polarization trend. On the one hand, the world's most active space powers are in this region, and on the other hand, there are still a large number of countries which do not have any space assets. According to the latest statistics, since 1960s, countries and regions along the BAR region have launched a total of 443 Earth observation satellites, 244 of them were launched by Europe. China and India have launched 87 and 42 EO satellites respectively among the all satellites. At present, countries along the BAR region possess a total of 160 in-orbit Earth observation satellites.
Space Earth observation technology has become the international community recognized modern social governance means. With the data democracy and data sharing movements promoted by international space cooperation and international organizations such as GEO, mastering application and analysis technologies to remote sensing data can also form a certain degree of space application capacity providing that data have been widely shared. Therefore, the right to use the space resource is available but space assets are not needed to be necessarily own. Due to the large amount and complex data analysis techniques of remote sensing data, the establishment of this capability is heavily dependent on the information infrastructure which is lacking in developing countries. It is very difficult to develop socio-economic management decision-making which based on remote sensing observation in these countries. Because they not only need to obtain remote sensing data provided by other countries through data sharing at first, but also able to download TB level remote sensing data internationally shared by low-speed network, as well as trying to conduct on-line analysis and processing the massive data on the desktops.
According to the abilities of space Earth observation and application of ground remote sensing data this two indicators, the countries and regions along the BAR region are divided into two major categories: data-rich countries and data-poor countries, about 30% of which are data-rich countries and about 70% are data-poor countries. Regional sustainable development requires synergistic and simultaneous development of countries and regions within the region, which claims that a primary and fundamental task of the Digital Silk Science Program is to improve the spatial application capacity in data-poor countries.
Progress in Cooperation
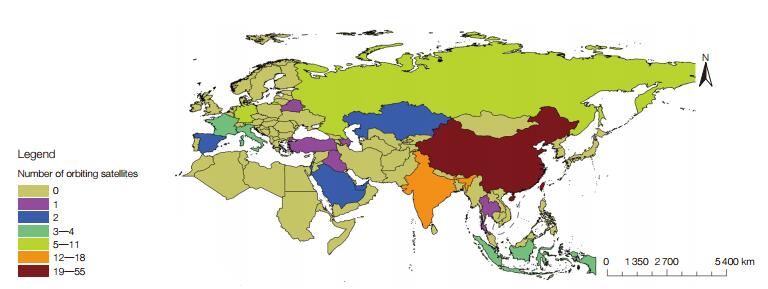
|
| Figure 1 In-orbit EO satellites statistics of BAR area |

|
| Prof. Li Guoqing (Director of Data Technology Division, Institute of Remote Sensing and Digital Earth, Chinese Academy of Sciences; Working Group Co-Chair of DBAR-DATA; Currently serving as the Scientific Committee member of World Data System (WDS); also co-chair of CODATA Task Group on Linked Open Data for Global Disaster Risk Research (LODGD); Director of China Earth Observation Data Sharing Platform (China-GEOSS); His PhD degree got from the Institute of Geographic Sciences and Natural Resources Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences in 2004) |
Based on the differences between the space earth observation capability and the application capacity of ground remote sensing data among the countries and regions along the BAR area, as well as the ongoing international data sharing work in this region, DBAR has established the Big Data Working Group (DBAR-DATA) to promote the building of the supporting capacity to the Earth observation data in order to overcome the data gap between datarich countries and data-poor countries, to enhance the spatial application capacity of data-poor countries, to support the realization of sustainable development goals in the BAR region. At present, experts from China, Italy, Spain, the United Kingdom (UK), Laos, Thailand, and the European Union have participated in the work of the DBARDATA, on behalf of many institutions and companies on space data service and application such as Chinese Academy of Sciences, National Satellite Meteorological Centre of China, National Supercomputer Center in Jinan, China RS, Ministers of the Ministry of Science and Technology of Lao P.D.R, Asia-Pacific Space Cooperation Organization, European Commission's science and knowledge service, the Joint Research Centre's mission (JRC), National Research Council of Italy, isardSAT, and so on.
Prof. Li considers that there are a large number of similar international projects and organizations in the world and among the countries and regions along the BAR area. The data sharing work of DBAR should fully understand and clarify the different positioning between the countries and regions along the BAR area, should actively join GEO, SCOSA, APSCO, and other International organizations and cooperation programs, through the joint design and common results to form a unique implementation route, as a result together to build the Belt and Road Remote Sensing Big Data Platform System. The key issue of DBAR-DATA is that DBAR should focus on solving the most pressing problems and the most realistic difficulties in remote sensing technology applications among these regional developing countries, consequently, improve their application ability substantially.

|
| Dr. Silap BOUPHA (Lao National Focal Point of ASEAN Subcommittee on Space Application (SCOSA), Co-Chair of DBAR-DATA Working Group and Assistant to the Ministers of the Ministry of Science and Technology on the matters of Science, Technology, and Innovation including ASEAN Affairs and Geo-space Technology and Applications) |
Dr. Silap BOUPHA points out that the ASEAN region is one of the fastest growing areas on global economic growth and human development, but it is also one of the world's most vulnerable regions to climate change impacts and a large scale natural disasters such as droughts, floods, earthquakes, tsunami, typhoons, volcanic eruptions, sea level rise, heat waves, also man-made disasters such as oil spills and haze/smoke, and also face the pressure of sustainable socio-economic development. ASEAN pays high attention and attach great importance to the role of space technology and application, satellite meteoroly and remote sensing data in addressing these issues and strongly hopes to develop and strengthen sustainable regional cooperation with the DBAR in priority areas, including urban development, disaster risk management, agriculture and rural development, environment and natural resources management and sustainable development, development planning, water, energy, food security and in all areas of space technology.

|
| Xu Zhe (Senior Engineer of National Satellite Meteorological Centre (NSMC)/China Meteorological Administration (CMA), the section chief of Data Management Division, focuses on meteorological satellite data archive and service system operation and data user support) |
Xu Zhe claims the process of obtaining and using EO data of countries along the BAR area, such as the CMACast technology used by the National Satellite Meteorological Centre of China on behalf of the China Meteorological Administration for the international sharing and service work of meteorological satellite data products, should be simplified. The system is a DVBS-2 data broadcasting system constructed by the China Meteorological Administration, and average daily distributes more than 220 GB of meteorological satellite data to more than 2, 000 subscriber station. Countries along the BAR region could receive real-time satellite data through CMACast receiving station. CMACast system is currently available in Iran, Bangladesh, Indonesia, Maldives, Nepal, Mongolia, Malaysia, Pakistan, Thailand, Philippines, Uzbekistan, Kyrgyzstan, Laos, Sri Lanka, North Korea, Vietnam, Myanmar, Australia, Kazakhstan, and other areas along the BAR area, which will become a very important data protection channel for DBAR (Figure 2).
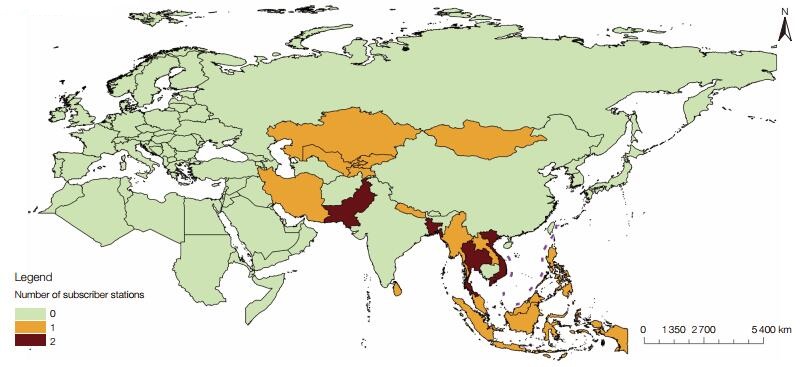
|
| Figure 2 CMACast users in the Belt and Road area |

|
| Prof. Stefano Nativi (Head of the Florence Division of the Institute of Atmospheric Pollution Research of the National Research Council of Italy, Scientific coordinator of the "Earth and Space Science Informatics Laboratory (ESSI-lab)" of CNR-IIA) |

|
| Dr. Joost van Bemmelen (over 25 years of experience in the field of software engineering and development of complex architectures and systems, and now working in ESA/ESRIN. Joost is and has been responsible for many EO mission ground segment development activities among which the GEOSS portal development) |
Prof. Stefano Nativi and Dr. Joost van Bemmelen argue that the core of space technology applications in all of countries and regions along the BAR area is the data sharing, and we should actively learn from the experience of GEO. GEOSS, developed by GEO, is a global and flexible network of content providers allowing decision makers to access an extraordinary range of data and information at their desk. The GEOSS Common Infrastructure (GCI) has implemented a software ecosystem by applying the upstream-midstream-downstream pattern to connect the users to the vast supply system: the GEO-DAB (Discovery and Access Broker) and the GEOSS portal play an important role to this end. Figure 3 depicts GEOSS discovery and access capabilities in a region like the one considered by the DBAR initiative. Through GEO's technical infrastructure, DBAR could directly use the international GEO data resources, could also dynamically use the data resources which show diversification within the region.
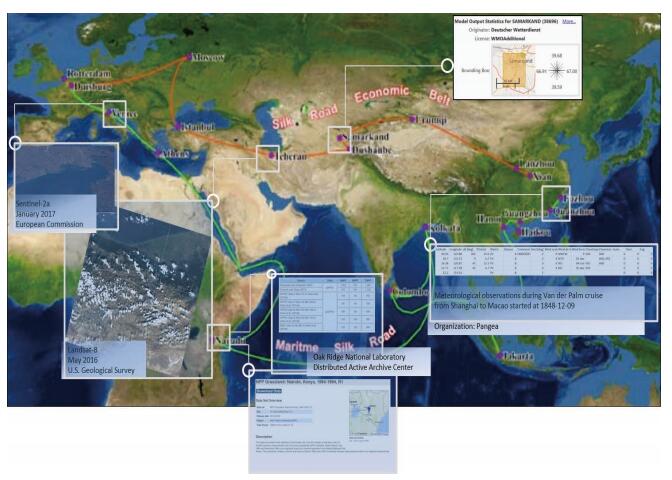
|
| Figure 3 GEOSS capabilities showing data records from different heterogeneous data resources that could be of interest to the DBAR initiative. |

|
| Dr. Guo Zhifeng (Senior Expert in the field of vegetation biophysical parameters inversion using multiple-sensor data, large-scale photogrammetry mapping and remote sensing data sharing and applications service integrating cloud service technology, he is serving as the head of international affair department of China RS Co. Ltd. He got his degree from CAS in 2005) |
Dr. Guo Zhifeng believes that data cloud services could greatly improve the convenience of data acquisition for data users in developing countries. On July 12, 2016, China RS Co. Ltd. developed the Remote Sensing satellite Data Cloud Platform for the Asia-Pacific Space Cooperation Organization, which provides remote sensing regional cloud services for a number of member countries. The shared data even contains 2 m resolution GF-2 satellite data and a number of Chinese latest Earth observation satellite data, which is the first time of remote sensing images, meter lever resolution, large-scale free sharing in all of the world (Figure 4). The development and going deep of this work will greatly facilitate the data sharing and data services capabilities of the DBAR.
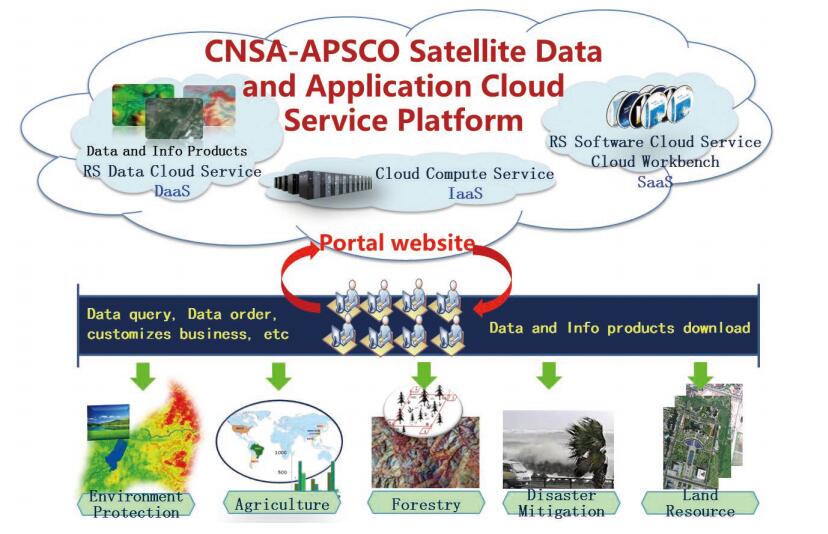
|
| Figure 4 CNSA-APSCO satellite data and application cloud service platform |

|
| Ms. Laia Romero (Director of Operations and Strategy at isardSAT Ltd., has more than ten years of specific experience in the design and operation of Earth observation applications and services for disaster risk management, hydrology, and climate change. One of her responsibilities is the implementation of the Thematic Exploitation Platform for Hydrology for the European Space Agency, coordinated by isardSAT). |

|
| Mr. Bernat Martinez (Engineer, Project Manager in isardSAT) |
Prof. Guo Huadong, the president of DBAR, believes that DBAR is a scientific, open, cooperative international initiative, and the engagement of private companies is also one of the directions of DBAR. Ms. Laia and Mr. Bernat from isardSAT Co. Ltd. think new ways of managing data are being developed and implemented energetically, user behavior and expectations are equally important and not straightforward. The idea of engaging communities, formed by different types of users around the same thematic, can represent one of the main breakthroughs for DBAR (Figure 5). In order to position Earth Observation data as a common and reliable practice for environmental and societal issues among the BAR area, the collaboration of leading scientific institutions and ICT innovative services and infrastructure, with the capacity of actively using global Earth observation data sources, will play a major role.
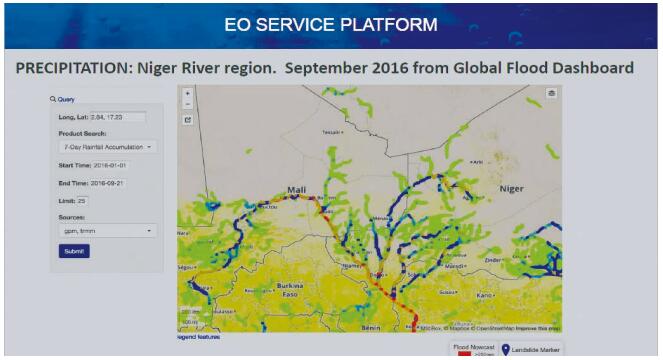
|
| Figure 5 Online hydrology analysis service in an isardSAT developed HEP cloud, designed for African hydrology communities |
At the just ended Kick-Off meeting of DBAR-DATA working group in early March of 2017, the experts from the member countries had in-depth discussions about the future and implementation of this big data platform. Prof. Li Guoqing introduced their prospection of DBAR-DATA Working Group.
(1) Based on the GEO data sharing principle and data resource system, DBAR-DATA will establish a knowledge portal of the regional comprehensive observational data for all around the BAR region, connect the virtual data resources inside and outside the region, collect and collate some of the best data sets with high quality and reliable service in the region, use the localization portal which is accord with regional culture and language characteristics to improve the level of data service utilization and depth within the sub-regions.
(2) Based on the powerful cloud storage and cloud computing facilities, regarding important remote sensing data resources as the unit, DBAR-DATA will distribute a set of Remote Sensing Data Online Cloud Processing Center which integrating data storage, high-speed access, local processing, and virtualization services, and form an alliance of the Remote Sensing Data Online Cloud Processing Centers, aiming at providing a powerful big data platform of data analysis and application for professional users in the BAR region under the premise of avoiding a large number of data network movement.
(3) Relying on the big data cloud computing facilities provided by the business data center, DBAR-DATA will select the moderate or low resolution data resources with clear and shared policies, build an online database which are the regional full space-time covering and continuous updating, take advantage of the less bandwidth consumption virtual machine mode to build a BAR remote sensing data education and training platform, which in order to provide the online support environments to the remote sensing courses and trainings of universities and public users in the regional developing countries.
(4) For all the users of the BAR region and the work groups and task groups of DABAR-DATA, on the basis of massive remote sensing data, combining value-added and information products formed from scientific and sustainable development issues, DBAR-DATA will process the delimitation of copyrighted publications and shared release through data publication, select influential results, regularly publish DBAR data product albums, train and the establish an orderly and open Remote Sensing Information Product Sharing Mechanism.
